Processes and engineering have remained a fundamental part of chemical plant design and surely will continue to be. Chemical engineering processes include thermodynamics, transport phenomena, reactor engineering, and process design and control. But advancing the fundamentals of process and product science and engineering is also essential to the vitality and effectiveness of chemical engineering.
According to the above, it is necessary to include five new areas in the design: process-product co-design, high-tech processes, analytics and automated learning, sustainability and the expansion of biotechnology.
Co-design process – product
Chemical engineers are increasingly involved in the design and development of new specialized products, formulations and materials whose properties are often sensitive or determined by optimal design and operational processes.
By integrating processing with product design in chemical plants, both processes can be enriched. Therefore, experts hope to establish particular methods and tools for the design and development of multifunctional materials such as catalysts, polymers, nanoparticles, among others.
Eventually, new tailored functional devices and products will be developed on a routine basis for different industrial sectors (chemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage). In addition, products manufactured using 3D printers will also be available in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
High-tech processes
Unit operations have represented a powerful concept in chemical plant design. However, additive manufacturing, for example, goes beyond existing unit operations.
Manufacturing products such as automobiles and appliances has been characterized by a mix of machining (subtractive manufacturing) and assembly, but additive manufacturing provides a degree of design flexibility that represents unprecedented opportunities for process integration, including the rapid creation of prototyping and manufacturing of consolidated parts with improved heat and mass transfer and reaction characteristics.
Where once there was a small set of polymers that could be 3D printed, many different materials can now be printed, including metals, biological tissues, and food.
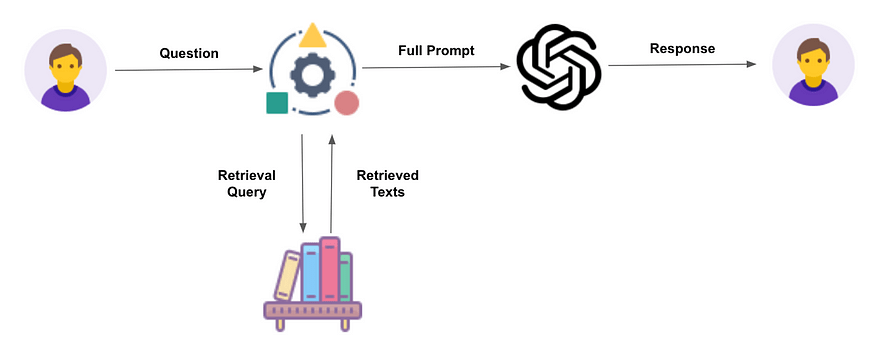
Analytics and machine learning
Products, operations and supply chains will change rapidly to benefit from the analysis of useful information in data, especially large data sets. The power of analytics will come from countless sensors that feed data through radio frequency identification and wireless technologies.
A broader application is smart manufacturing, which enables improvements in business and operational decision making through data analysis. Highly automated processes and controls will produce a level of data output and connectivity that has not been seen before in the industry, which could connect directly with consumers and perhaps move further towards personalized medicines.
Sustainability
Analyzing the long-term result of the social, environmental and financial impact is the basis of decisions oriented to sustainability about products and processes in chemical plants. Decisions based on sustainability can become the norm, relying on responsibility for decisions that can affect us now and for generations to come.
For example, most countries and industries have accepted that we will have to cope with the effects of climate change while, in recent years, companies have been recording the harmful effect of future climate change as they have to prepare to operate in a more challenging environment. For manufacturing, adaptation requires protection of infrastructure, alteration of processes and raw materials, and management of supply chains.Stalwart International – India?s largest manufacturer and exporter of Chemical Process Equipment